Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a common hormonal disorder that affects women of childbearing age. It is characterized by irregular menstrual cycles, excess hair growth, acne, and infertility. PCOS can also cause other health problems, such as obesity, type 2 diabetes, and heart disease.
What is PCOS? PCOS Cause, Symptoms, treatments
Causes of PCOS
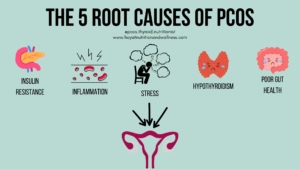
The exact cause of PCOS is unknown, but it is thought to be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Some of the possible causes of PCOS include:
- Genetics: PCOS can run in families, suggesting that there is a genetic component to the disorder.
- Insulin resistance: Many women with PCOS have insulin resistance, which means that their cells do not respond normally to insulin. Insulin is a hormone that helps the body to use sugar for energy. When cells are resistant to insulin, the body produces more insulin in an attempt to compensate. This high level of insulin can lead to excess androgen production and other PCOS symptoms.
- High levels of androgens: Androgens are male hormones that are also produced in women. Women with PCOS tend to have higher levels of androgens than women without PCOS. This can lead to excess hair growth, acne, and other masculine-looking features.
Symptoms of PCOS

The symptoms of PCOS can vary from woman to woman. Some of the most common symptoms include:
- Irregular menstrual cycles: Women with PCOS may have irregular menstrual cycles, meaning that they may skip periods or have very light or heavy periods.
- Excess hair growth: Women with PCOS may experience excess hair growth on the face, chin, chest, abdomen, and back.
- Acne: Women with PCOS are more likely to develop acne than women without PCOS.
- Infertility: PCOS is a leading cause of infertility in women.
- Other health problems: PCOS can also increase the risk of other health problems, such as obesity, type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and stroke.
Treatments for PCOS

There is no cure for PCOS, but there are treatments that can help to manage the symptoms and reduce the risk of complications. Treatment options may include:
- Lifestyle changes: Lifestyle changes, such as losing weight, eating a healthy diet, and exercising regularly, can help to improve symptoms and reduce the risk of complications.
- Medications: Medications can be used to regulate menstrual cycles, reduce hair growth, improve acne, and treat other PCOS symptoms.
If you are concerned that you may have PCOS, it is important to see a doctor for diagnosis and treatment. Ladies, don’t miss your yearly check-up!